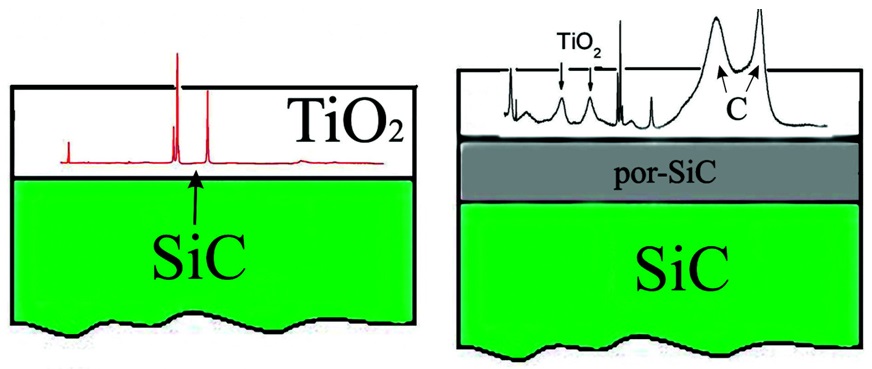
Regardless of the substrate structure, the obtained
TiO2 layers are formed with the composition close to the stoichiometric one.
In the SiC/por-SiC/TiO2 structures the
graphite phase is formed at the por-SiC/TiO2
interface, which degrades the quality of this interface
The presence of a porous layer makes it possible to
enhance the Raman signal from a thin TiO2 film.
Semiconductor Physics, Quantum Electronics & Optoelectronics, 21 (2), P. 200-205 (2018).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15407/spqeo21.02.200
Comparison of properties inherent to
thin titanium oxide films formed by rapid thermal annealing on SiC and
porous SiC substrates
Yu.Yu. Bacherikov1, |_N.L. Dmitruk_|1, R.V. Konakova1, O.F. Kolomys1, O.B. Okhrimenko1*, V.V. Strelchuk1, O.S. Lytvyn2, L.M. Kapitanchuk3, A.M. Svetlichnyi4
1V. Lashkaryov Institute of Semiconductor Physics, NAS of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine
2Borys Grinchenko Kyiv University, Kyiv, Ukraine
3Paton Institute of Electric Welding, NAS of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine
4Institute of Nanotechnologies, Electronics, and Electronic Equipment Engineering,
Southern Federal University, Taganrog, Russia
*E-mail: olga@isp.kiev.ua
Abstract. The comparative analysis of optical characteristics inherent to TiO2/SiC and TiO2/por-SiC/SiC structures has been performed. It has been shown that, in these structures regardless of the substrate structure, formation of TiO2 layers with approximately the same width 60 nm takes place. In this case the TiO2 film composition is close to the stoichiometric one. At the same time, the presence of an additional porous layer in the TiO2/por-SiC/SiC structure leads to blurring the oxide film – substrate interface but promotes an increase in the intensity of the Raman scattering signal from the oxide film.
Keywords: thin titanium oxide films, SiC substrates, interface, porous layer.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.